“It’s immense,” said Sara Faggi, a planetary astronomer at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center.
Scientists caught Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus spraying a “huge plume” of watery vapor far into space — and that plume likely contains many of the chemical ingredients for life.
Scientists detailed the eruption — glimpsed by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) in November 2022 — at a conference at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore on May 17.
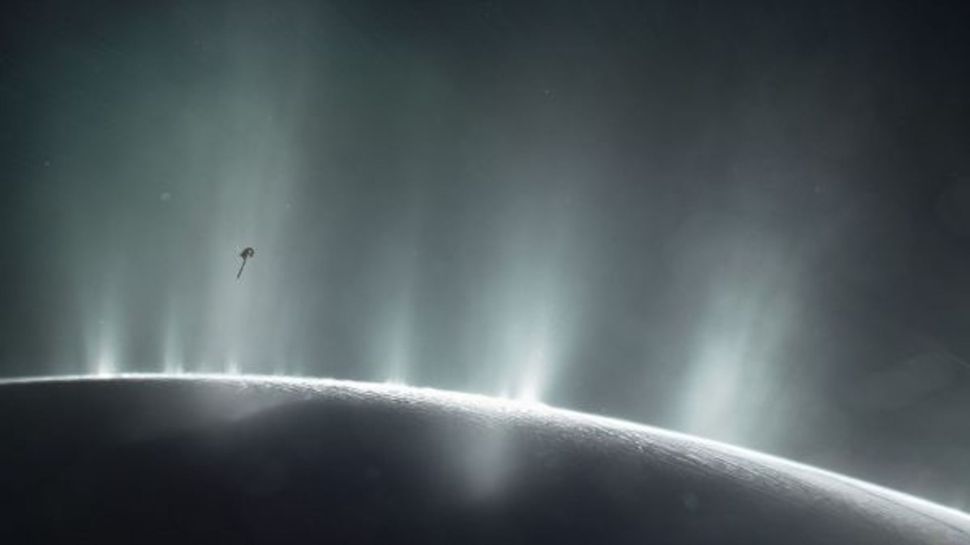

“It’s immense,” Sara Faggi, a planetary astronomer at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, said at the conference, according to Nature.com. According to Faggi, a full research paper on the massive plume is pending.
This isn’t the first time scientists have seen Enceladus spout water, but the new telescope’s wider perspective and higher sensitivity showed that the jets of vapor shoot much farther into space than previously realized — many times deeper, in fact, than the width of Enceladus itself. (Enceladus has a diameter of about 313 miles, or 504 kilometers.)
Scientists first learned of Enceladus’ watery blasts in 2005, when NASA’s Cassini spacecraft caught icy particles shooting up through large lunar cracks called “tiger ᵴtriƥes.” The blasts are so powerful that their material forms one of Saturn’s rings, according to NASA.

Analysis revealed that the jets contained methane, carbon dioxide and ammonia — organic molecules containing chemical building blocks necessary for the development of life. It’s even possible that some of these gases were produced by life itself, burping out methane deep beneath the surface of Enceladus, an international team of researchers posited in research published last year in The Planetary Science Journal.
Water is another piece of evidence in the case for possible life on Enceladus. Enceladus is totally encrusted in a thick layer of water ice, but measurements of the moon’s rotation suggest that a vast ocean is hidden beneath that frozen crust. Scientists think the spurts of water sensed by JWST and Cassini come from hydrothermal vents in the ocean floor — a hypothesis supported by the presence of silica, a common ingredient in planetary crusts, in the vapor plumes. 
NASA scientists are discussing future return missions to seek out signs of life on Enceladus. The proposed Enceladus Orbilander would orbit the moon for about six months, flying through its watery plumes and collecting samples. Then, the spacecraft would convert into a lander, descending on the surface of the icy moon. Orbilander would carry instruments to weigh and analyze molecules, as well as a DNA sequencer and a microscope. Cameras, radio sounders and lasers would remotely scan the moon’s surface, The Planetary Society reported.
Another proposed mission involves sending an autonomous “snake robot” into the watery depths below Enceladus’ surface. The robot, dubbed the Exobiology Extant Life Surveyor, features cameras and lidar on its head to help it navigate the unknown environment of Enceladus’ ocean floor.